Estate Planning Definition Video
Estate Planning Definition
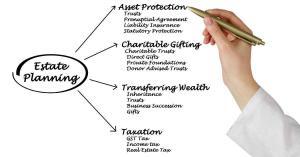
The part that people get right about an estate planning definition is that estate planning is about distributing your property, your final estate, to others. That definition misses many important things a plan also does.
Estate planning also includes
- Nominating guardians for minor children
- Naming an executor
- Making healthcare choices now instead of making family guess later
- Naming somebody to manage your financial, legal, and healthcare affairs if you can’t
- Planning for mental incapacity
- Tax planning
- Taking care of children with special needs
- Taking care of children with addictions to alcohol, drugs, or anything else
- Protecting children from their creditors
- Protecting children from their spouses
Estate planning is as much about protecting you and your family during your lifetime as it is about preventing the ordeals of probate. Estate planning is about you keeping control over your affairs and property in case of incapacity. It is about ensuring your wishes for managing your affairs and property are upheld.
It is essential that you have a durable power of attorney and a healthcare power of attorney in addition to a Will or Trust. If you don’t then your lifetime protection is limited. If you don’t plan for lifetime protection, then undesired family and the courts may take over making your decisions. If nobody else steps up, then it could be Adult Protective Services.
Estate planning is the process of creating instructions about handling your affairs and your assets in the case of your mental disability or incapacity, legal incapacity, or when you pass.
This is very similar to the estate planning definition found here. And Wikipedia defines estate planning as: Estate planning is the process of anticipating and arranging, during a person’s life, for the management and disposal of that person’s estate during the person’s life and at and after death, while minimizing gift, estate, generation skipping transfer, and income tax.
